Cutting trees on a massive scale has made deforestation a top environmental priority, both at the local and global...
If we ignore forest, we must understand that without forests, we cannot have biodiversity. We cannot regulate our climate without biodiversity, and we cannot sustain resources to our communities without that.
With the increasing problems of deforestation and environmental degradation hitting the world today, this has brought great recognition for sustainable forest management.
One of their most effective ways of protecting or restoring forests is the so-called Community Forests wherein local communities become collectively responsible for the management and maintenance of forest resources.
This is one of the grassroots empowering initiatives where community forestry contributes sustainability, a greater boost in biodiversity, and enhancement of local economies.
Understanding Community Forests
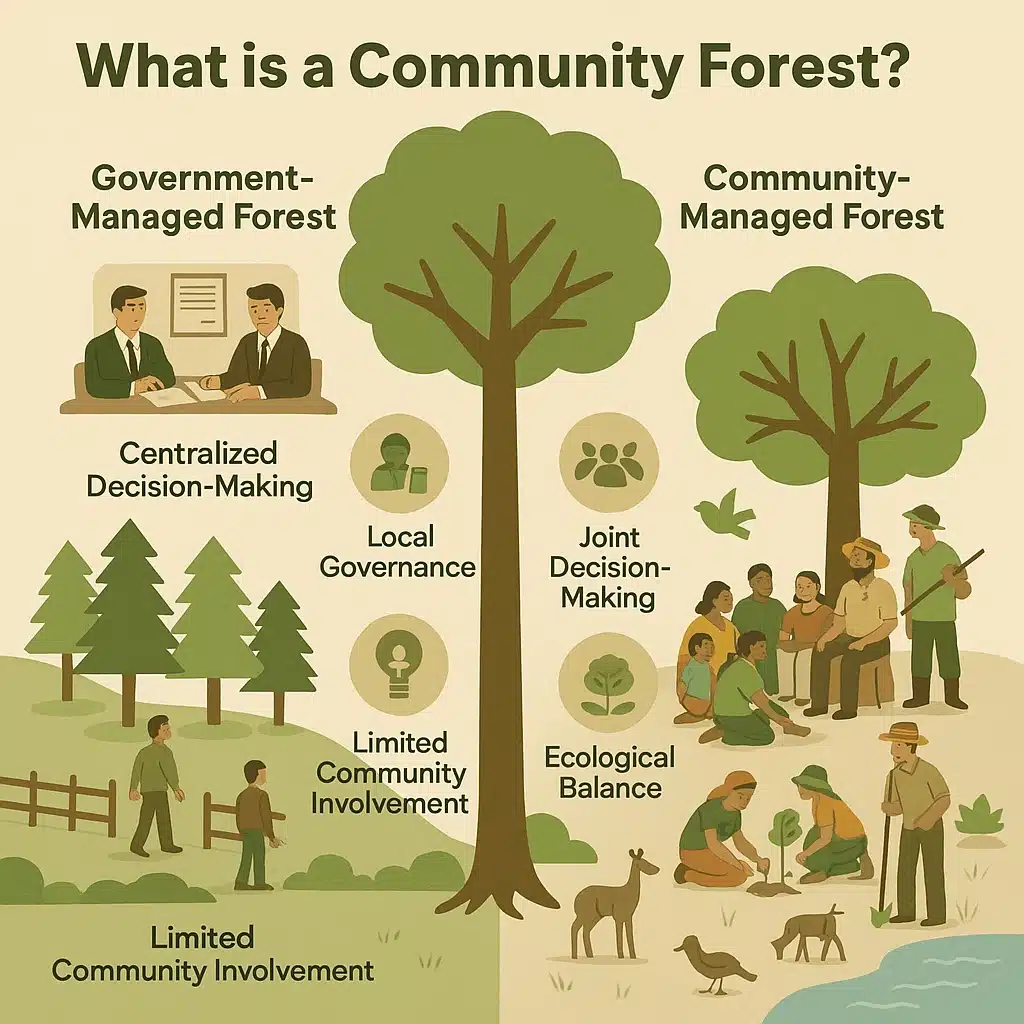
What Are Community Forests?
Community forests define rather than audience forests when local communities manage forests jointly with one another. Unlike conservation programs controlled by government agencies, these forests are managed by local residents who are active in making decisions that influence them from engaging in both ecological and economic aspects of life.
Such models attach conservation linkage with the lifeline of the people to be effectively and sustainably protected.
The Role of Community Involvement in Forestry
Community Involvement in Forestry is the basic pillar of community forest success in establishment and management. Bringing local people to conserve a forest creates ownership and responsibility towards the forest.
It assumes various forms, including tree planting, sustainable harvesting, wildlife protection, or even ecological monitoring. Benefits directly accruing to people from conservation of forest ecosystems motivate them to invest their efforts and time in preserving these ecosystems.
Benefits of Community Forests

1. Conservation and Sustainability
A major advantage of Community Forests is the role they play in Forest Conservation. They have been overexposed in terms of deforestation as compared to government-managed forests. That particular community has classified sustainable harvests and all things dealing with use and non-use.
2. Economic Empowerment
Potential income generating activities from community forestry include eco-tourism, honey production, and handcrafting products for sale. Employment is created from such activities while the economic well-being among local people improves.
3. Biodiversity Protection
Since communities depend on forests for their livelihoods, they will, by nature, take action to prevent overexploitation. Accordingly, beyond harvesting activities, local communities are able to protect wildlife, plant species, and water sources better. There have been many demonstrations in countries where Joint Forest Managements have been successful in saving biodiversity.
4. Climate Change Mitigation
Forests function as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide and thereby mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Communities managing forests act as sustainable protectors for the global fight against climate change.
Social Forestry and Joint Forest Management

The Concept of Social Forestry
Soil and tree management through the people’s participation is called Social Forestry. In several countries, this type of afforestation is merged into social development. This philosophy gives life and recreation opportunities in recovering degraded ecosystems.
Joint Forest Management: A Collaborative Approach
Joint Forest Management (JFM) is a strategy based on collaboration between governments and communities in protecting and regenerating forests.
According to a typical JFM agreement, community rights to forest resources are negotiated in exchange for participation in conservation activities. This model is successful in balancing environmental and economic needs in many parts.
Case Studies of Successful Community Forests
1. Nepal’s Community Forestry Program
Nepal is a global leader in community forestry, with over 22,000 user groups managing nearly 40% of the country’s forests. The initiative, therefore, increased forest cover and improved biodiversity and rural economies.
2. India’s Joint Forest Management Success
In India, JFM has empowered local communities to manage conservation, and consequently, there has been improved forest protection and resource management. Several states in India have witnessed remarkable ecological recovery owing to this partnership approach.
3. Mexico’s Community Forest Enterprises
The Mexican model of community-owned forest enterprises shows that sustainable logging, tourism, and agroforestry can all be income-generating activities benefiting forests. These enterprises are now the benchmark for community-driven conservation.
How to Start a Community Forest
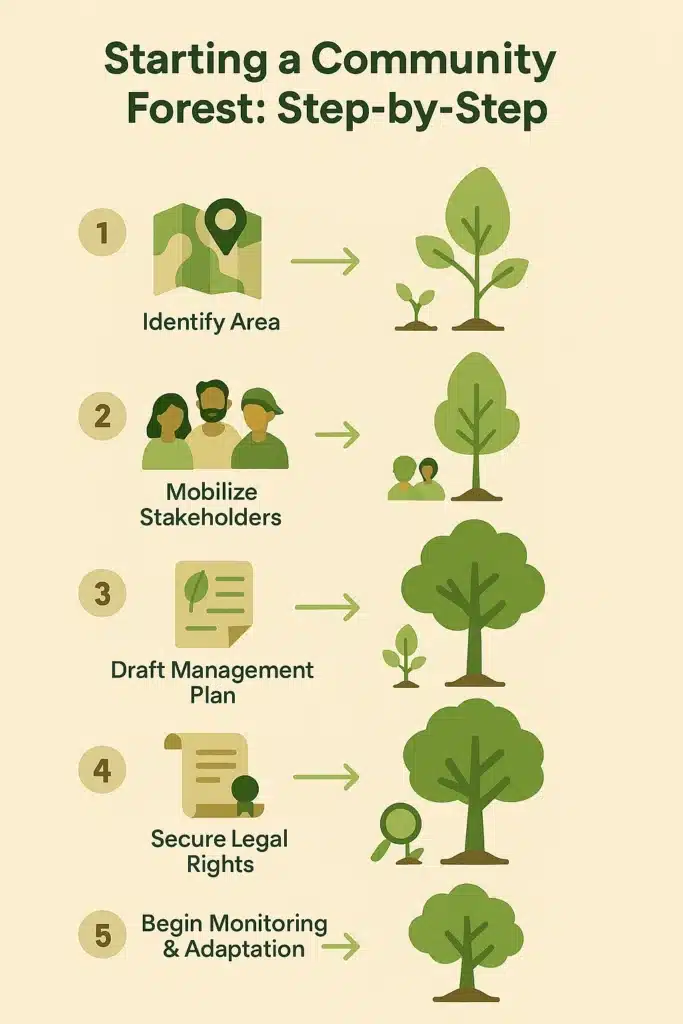
Steps to Establishing a Community Forest
If your goal is that of setting up a community forest, you can do these things:
- Identify a Suitable Area – The selection of a degraded forest area or underused forest area should consider where community management could make a difference.
- Mobilize the Local Stakeholders – Collaborate with community members, local authorities, and conservationists.
- Prepare a Management Plan – Establish rules for sustained use, conservation, and resource allocation.
- Secure Legal Recognition – Approach government bodies or environmental organizations to secure legal rights over forest management.
- The bylaws shall promote the process of afforestation, sustainability in harvesting, and protection of biodiversity.
- Monitoring and Adaptive Implementation- The health of the forests will be a subject of periodic review and practices will be adjusted for achieving greater sustainability.
How Can You Get Involved in Community Forestry?
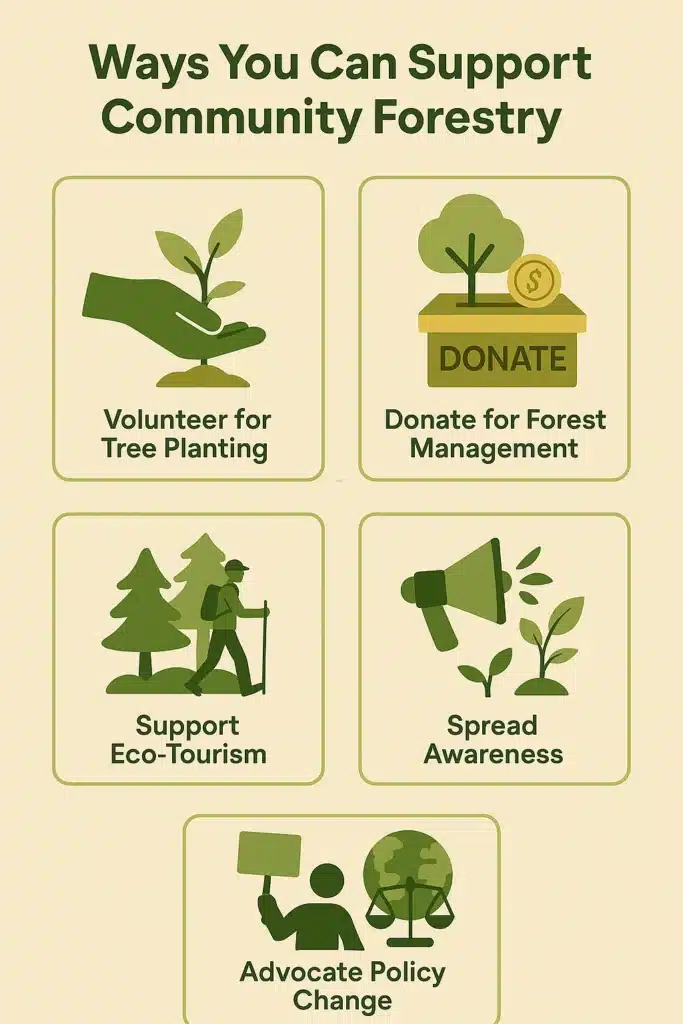
These are some ways of contributing to Community Forests even if one does not belong directly to a forest community:
- Support organizations dedicated to promoting community forestry initiatives.
- Participate as a volunteer in tree-planting campaigns/conservation projects.
- Advocate for policies that will enable communities to manage their resources.
- Inform others regarding the benefits derived from community-based conservation.
Conclusion
The future of our forests lies in collective action. Community forests provide a sustainable modality of addressing both environmental conservation and human uses. Such partnerships with local communities in forest stewardship protect natural ecosystems and promote economic growth and social well-being.
Whether one is a policymaker, environmentalist, as well as a member of a concerned populace, joining hands with communities in conservation activities is a step toward a greener and more sustainable future.
Our forests and our planet are going to survive for many generations with the help of togetherness.




