Across India, borewells are drying up, water tankers have become a daily reality, and groundwater levels are falling year...
At this moment, one of the biggest global challenges is not having enough water. In India, more than 600 million people experience severe to extreme difficulties with water, and climate change together with fast-paced urbanization are likely to make it worse.
To address this, planting drought-resistant trees can support local microclimates and reduce water demand. Here are 10 water-conserving trees ideal for Indian cities.
Taking this information into account, rainwater harvesting turns out to be a quick and effective way to tackle this challenge. It is easy for anyone to access, costs little, and can increase in size—so it’s perfect for communities and educational systems.
It is intended to be a useful guide for anyone who wants to perform rainwater harvesting, giving priority to school projects and community programs.
If you work as a teacher, a planner, or in any NGO such as Youth Talent Development Society (YTDS), using these ideas can have a real impact right away.
What is Rainwater Harvesting?
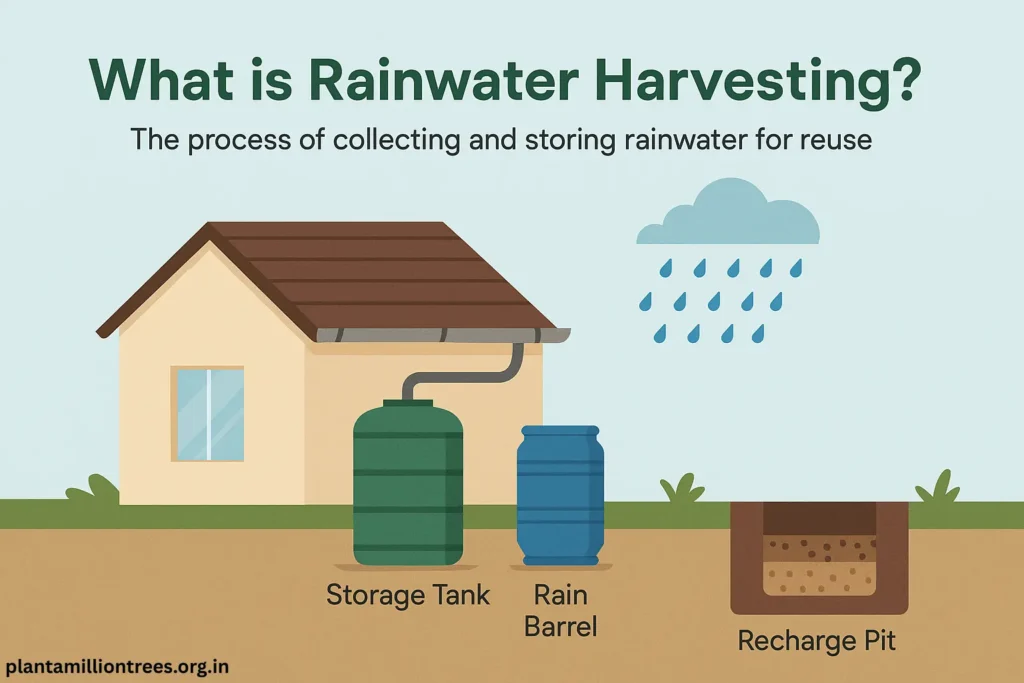
That process of collecting and saving rainwater from rooftops, roads, or similar areas to reuse is called rainwater harvesting. With this method, it’s easier to save water and help the environment, mostly in places where clean water is reserved for drinking.
Trees also play a powerful role in sustaining the water cycle. Explore how trees naturally support groundwater recharge and rain systems.
There are different systems used for rainwater harvesting.
- Rain falling on the roof can be collected into pipes and is sent either into storage tanks or into pits for recharging groundwater.
- Percolation Pits: Such pits are made by digging deep with gravel and sand so rainwater can soak into the ground and increase the groundwater supply.
- Wells are used to pump harvested water underground to help increase the levels of groundwater.
- Rain Barrels: They catch rainwater from downspouts for usage in the garden and at home.
Each design can use a combination of these methods, selected according to how big the project is, the site’s characteristics, and the purpose of the captured water.
Rainwater Harvesting Projects for Schools
Learning about water conservation can best happen in schools since it is an active way of learning. Listed below are 2–3 rain harvesting plans that can be carried out easily in schools by spending little money.
1. Rooftop system used to capture rainwater

Materials Needed:
- PVC gutters together with downpipes
- First-flush diverters
- Mesh filters
- For storage of the liquid, a tank (1000–5000 liters) is used.
Process:
The rain that collects on the school roof is passed through filters and put into tanks. Such water can be used for the following purposes:
- Toilet flushing
- Garden water systems in schools
- General cleaning
Outcomes:
- Over thousands of liters of water are saved each year.
- Greater attention about the environment by students
- The possibility to add nature education and science into teaching materials
2. The Rain Garden Project.
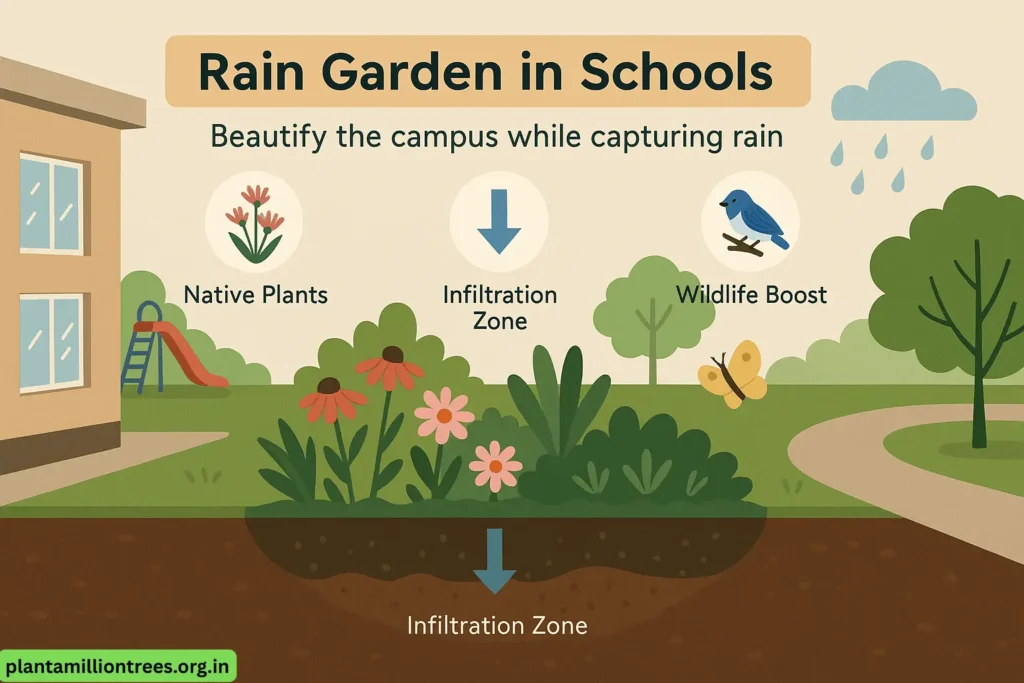
A rain garden is like a low spot with plants placed to gather water from nearby impermeable areas, parking lots or playgrounds.
Benefits:
Brings beauty to the school environment Boosts the amount of local wildlife There is less stormwater runoff.
3. The Percolation Pit
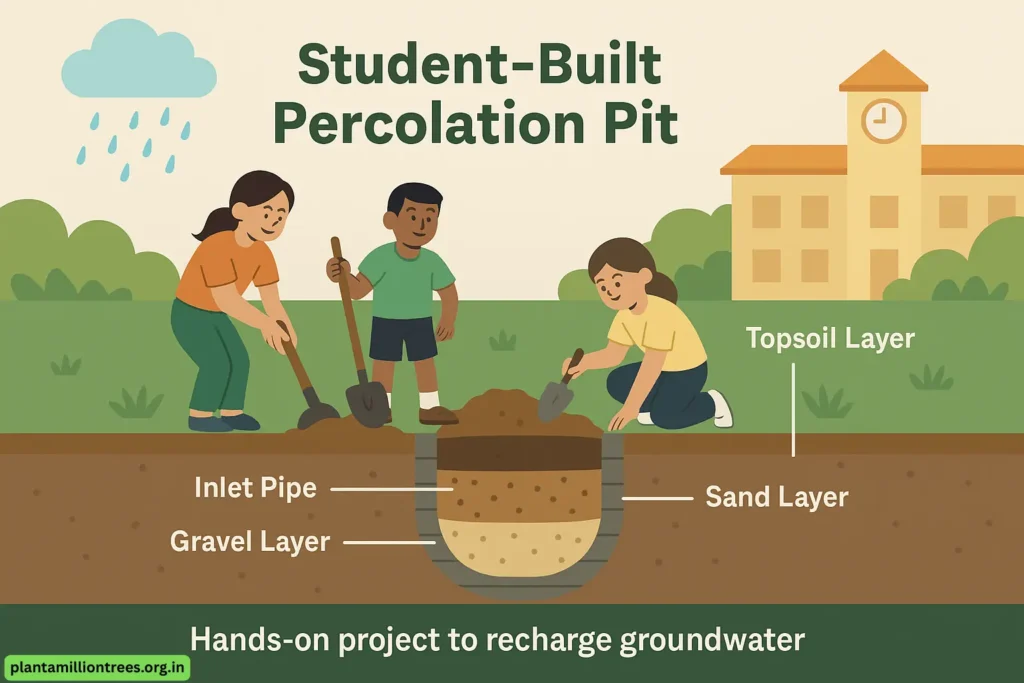
To assist, students could team up to build little percolation pits on the grounds so rainwater can return to the soil.
Materials:
- Types of gravel, coarse sand, and topsoil
- The pit walls should be formed with bricks or concrete rings.
Outcome:
To realize how important it is to recharge groundwater using a field experience.
Community-Level Rainwater Harvesting Projects
Raising the level of rainwater harvesting over various rural buildings and urban Smart Cities projects saves water and helps the community in many ways.
1. Rainwater Recharge Stations in Public Parks
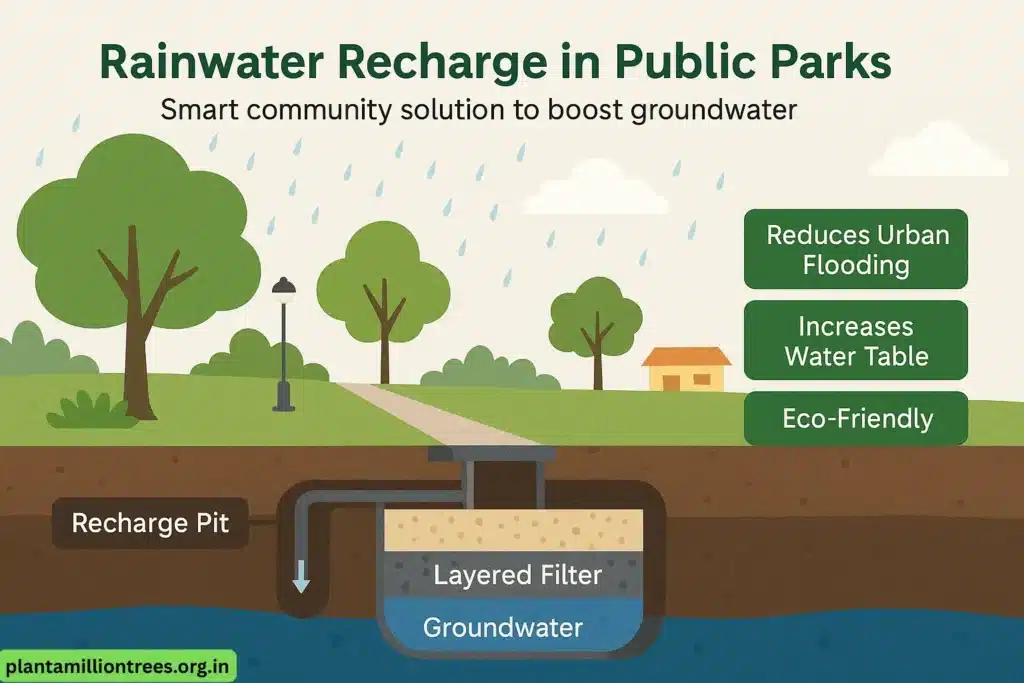
Implementation:
- Find big outdoor areas that are available to use.
- Make recharge pits that have several layers to filter the wastewater.
- Link roof-top systems to the pits that are close by.
Advantages:
- Boosts the quantity of groundwater in the area
- Handles the problem of urban flooding.
- Can be applied in civic planning at a reasonable price
2. Small structures that catch rainwater located at the side of roads
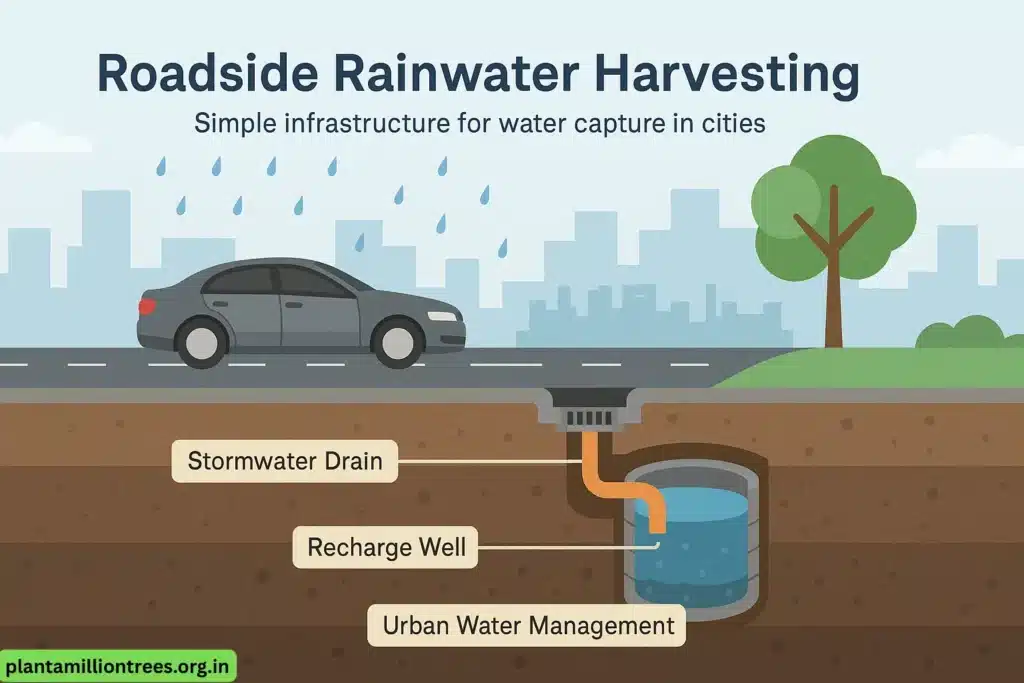
Concept:
Put in roadside rain traps at the entrances to stormwater drains. If there is a lot of rain, let the water go into recharge structures.
Case Study:
Within 2 years in Chennai, the pilot project for roadside rainwater harvesting increased the groundwater level by 15%.
Shared Rainwater Harvesting System in Residential Societies
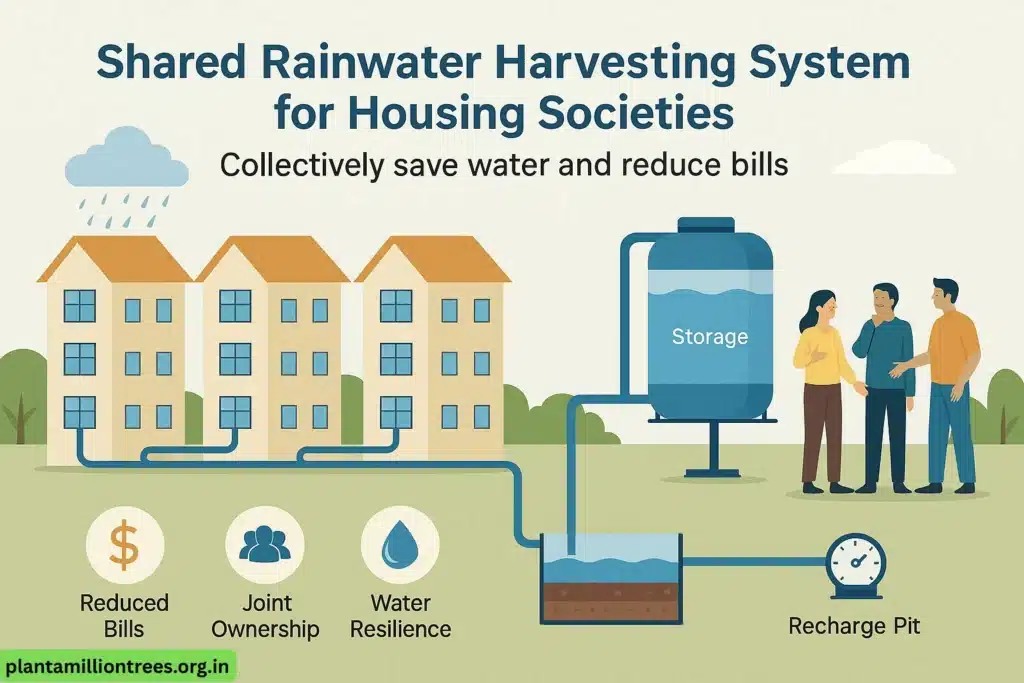
Concept:
Residential complexes can collectively install a rooftop rainwater harvesting system that distributes filtered water to each building or stores it in a shared tank or recharge well.
Implementation:
- Engage the RWA (Resident Welfare Association) to lead the initiative
- Channel rooftop water to a central filtration system
- Direct it into a shared storage tank or percolation pit
- Include a water meter to track savings
Advantages:
- Reduces collective water bills
- Encourages joint responsibility for water use
- Perfect model for apartment complexes or gated societies
Rooftop-to-Rain Barrel or Well Systems for Homes and Rural Areas
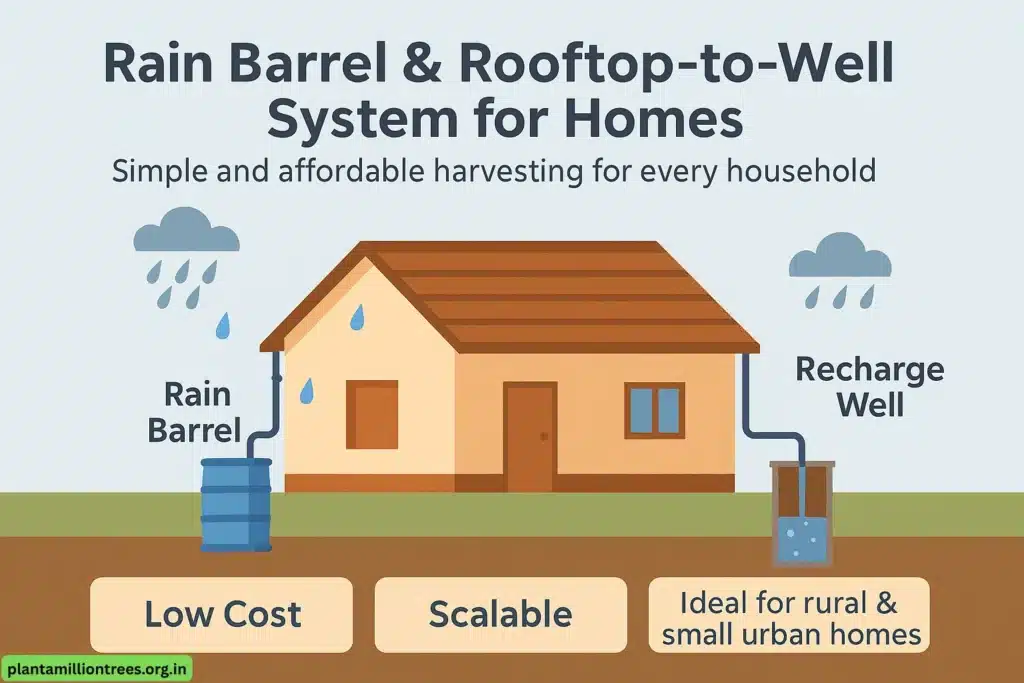
Concept:
Even small buildings in urban or rural areas can set up individual rooftop rainwater harvesting systems that collect rainwater into rain barrels or channel it directly into a shallow well for later use or groundwater recharge.
Implementation:
- Use a rooftop as the catchment area.
- Install mesh filters to screen debris.
- Channel water via PVC pipes into:
- A Rain Barrel for garden or domestic use, or
- A Recharge Well to increase local groundwater levels.
Advantages:
- Very low cost and easy to maintain
- Ideal for homes, small community centers, or rural schools
- Supports water conservation in both drinking and non-drinking uses
- Can be installed in areas with space limitations
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting projects bring many different positive results.
- By taking advantage of collected rainwater, each example avoids wasting a huge amount, thus lessening reliance on the water provided by your local municipality or borewell.
- Urban areas have to pay special attention to flood control. Rainwater harvesting lowers the impact of runoff and helps prevent pressure on drains.
- Plummeting groundwater in many Indian communities is reversed through rain water harvesting within the community.
- Harvested rainwater helps save money by letting families, schools, and entire communities use it instead of buying expensive treated water for several uses.
Example from India: The Delhi Jal Board estimates that effective rainwater harvesting can reduce water demand by up to 30% in high-consumption areas.
How to Execute Your Rainwater Harvesting Project
If you’re planning a DIY setup, check out our Rainwater Harvesting at Home: Step-by-Step Guide for a detailed walkthrough.
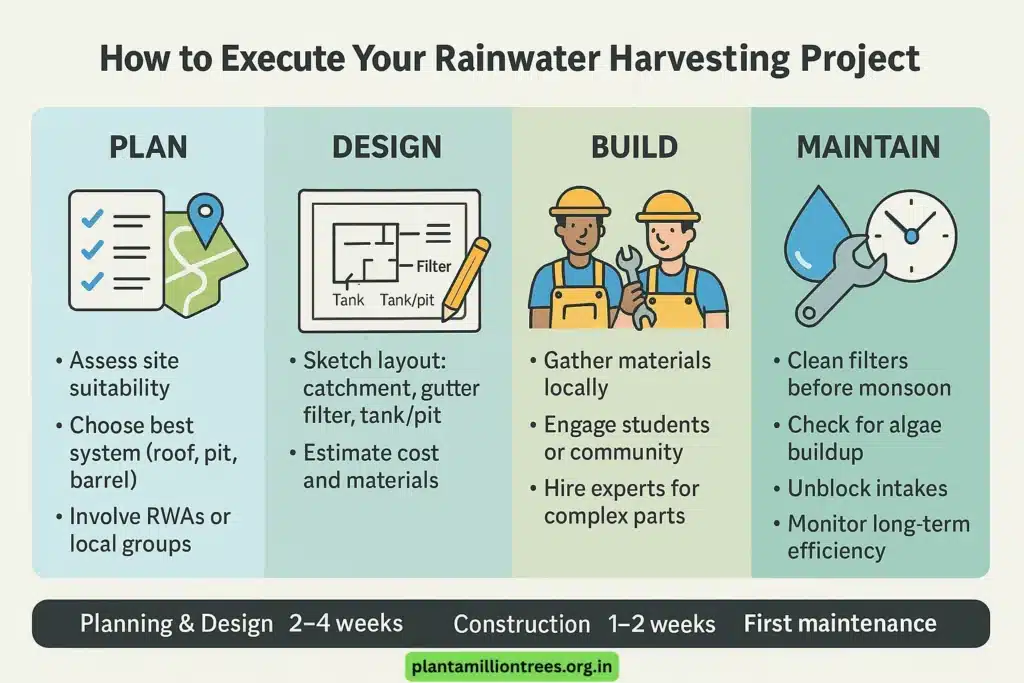
How to create a rainwater harvesting system one step at a time:
Plan:
- Check the suitability of the site for rainwater collection so that you know how much can be collected.
- Select the best type of rain collecting system for your household (rooftop, pit, barrel, and so on).
- Include the management, RWAs, or groups in your community.
Design:
- Typify a layout for your system.
- Catchment area
- The transport system consists of gutters and pipes.
- Filtration mechanism
- You need to choose between a storage tank and a recharge pit.
- Make an estimate of what the project will require.
Build:
- Get materials from local suppliers.
- Let students or the wider community help with easy chores (clear the site, put the filters in place).
- For tricky installations, hire those with proper experience.
Maintain:
- Carry out regular seasonal maintenance for your car.
- The car’s filters should be cleaned just before monsoon begins.
- Go through the stored stock to see if there are signs of algae.
- Unblock any objects in the intake for the system.
- Develop a strategy to keep an eye on the efficiency of the system for its life span.
Timeline Example:
- At this stage, planning and design activities take place for 2 to 4 weeks.
- It should take one to two weeks to finish construction.
- The first maintenance should be done before the monsoon season
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Finding out about typical errors is necessary before you begin any kind of rainwater harvesting project.
- Debris and pollution enter the water tank or block the system’s filters when the filtration is poor. Make sure to buy a mesh filter and first-flush diverter that are high in quality.
- If the pond is not regularly taken care of, dirt and algae will collect inside the filtration system. If you have a maintenance schedule in place and everyone knows what they need to do, it will protect you from scammers.
- It’s important not to overlook water balance; the model should be designed to fit the amount of rainfall in your location and the needs for that water.
Pro Tips:
- Equip the storage tanks with current water level showing indicators.
- Make use of signs and encourage students to take part, as this can enable them to feel responsible for their learning.
- Along with installing devices, community rain harvesting should include promoting programs to inform everyone.
Conclusion
Since water scarcity is an issue now, everyone must practice rainwater harvesting for its essential benefits. You can rely on these tools and ideas for rainwater harvesting to begin anything from a school program to recharging systems at the community level or just a small project.
According to YTDS, fighting for safe drinking water begins with the community stepping in. Little by little makes a difference. When you practice rainwater harvesting, you help both nature in your area and the country’s environmental plans.
Try to start with little steps, envision great projects, and encourage people around you. The following achievement in rainwater harvesting could begin by setting an example yourself.




